What are SBA Loans?
The SBA loan program consists of several financing packages designed to meet the needs of small business owners. The US Small Business Administration (SBA) runs the program, sets guidelines and limits for lenders, and partially guarantees the loans.
Since the government agency partially backs the loans, lenders have less risk and can offer higher borrowing amounts at lower interest rates and longer repayment terms. The SBA further helps reduce financing costs by setting maximum interest rates that lenders can charge.
The SBA does not approve SBA loans or issue funding (with a few exceptions). Instead, small business owners apply to one of three lending institutions: commercial banks, credit unions, or alternative lending facilitators like United Capital Source.
The most common and popular SBA loan is the 7(a) loan. The maximum borrowing amount for 7(a) loans is $5 million. Terms go up to 25 years for real estate loans and 10 years for most other loans. There are several subsets of the 7(a) loan program, including express loans, export lines, CAPLines of credit, and the pilot program Community Advantage loans.
Each subset of the 7(a) loan program has a different borrowing amount. Interest rates are pegged to the prime rate plus the lender’s spread. The maximum interest rate depends on the loan amount, maturity, and whether it’s a fixed or variable-rate loan. You can get a complete overview of 7(a) loans, borrowing amounts, interest rates, and terms.
Uses of SBA 7(a) loans include:
- Purchasing commercial real estate.
- Working capital needs.
- Purchasing inventory.
- Buying equipment, machinery, or other fixed assets.
- Refinancing business debt.
Other SBA loans include:
What is SBA Form 413?
SBA Form 413 is a “Personal Financial Statement.” SBA loan applicants complete the form as part of their application for SBA 7(a), CDC/504 loans, and Microloans.
On the form, potential borrowers will identify the following:
- Basic identifying information.
- Assets and liabilities.
- Sources of income.
- Debts owed to banks for other institutions.
- Stocks and bonds.
- Any real estate owned.
- Other personal property or additional assets.
- Any unpaid taxes or tax liens.
- Other liabilities.
- Life insurance policies.
Why does the SBA require Form 413?
While the SBA-approved lender ultimately approves and underwrites the loan, the SBA still must agree to cover the guaranteed portion. Approval from the SBA does not mean you’re approved for a loan, but it is a necessary step in the approval process.
When assessing a loan application, the SBA determines your creditworthiness by analyzing both your personal and business financials. Business assets and liabilities are covered in other required documentation, but Form 413 is how the agency assesses your personal finances. Failure to complete and file Form 413 could result in your loan application being denied.
Who needs to complete Form 413?
As previously stated, Form 413 is required for SBA 7(a) and 504 loan applications. The specific business partners required to complete the form depend on the type of business entity, i.e., sole proprietorship, partnerships, limited liability companies (LLCs), and others.
Each of the following people must complete the form:
- Each proprietor of the business.
- Each owner with at least a 20% stake in the company.
- Each general partner.
- Each managing member, if an LLC.
- Any other party guaranteeing the loan.
Married applicants must also include any assets and liabilities from their spouse or minor children. If the applicant has a prenuptial agreement or any other arrangement that legally separates their assets, it is not required to include them.
How do I complete Form 413?
Before filling out the form, it would be best to prepare the supporting documents for your assets and liabilities. You’ll need to include these documents as proof on your form, and it will be easier to record the information on the form if they’re already prepared.
Documents Required for Assets & Liabilities
For listing your assets, you should prepare the following:
- Bank statements for checking, savings, or other bank accounts.
- Statements for IRA, 401(k), or other retirement accounts.
- Any current loan agreements or promissory notes for any money you’ve lent to others.
- Life insurance policy and any savings accounts.
- Net investment income statements for stocks, bonds, or other securities.
- Any deeds, insurance policies, and current market values for owned real estate.
- Real estate income.
- The current market values of any vehicles you own.
- Personal property values on jewelry, artwork, or antiques.
- Financial information for any additional personal assets not listed above.
For listing liabilities, you should prepare the following:
- Any loans or accounts payable for debts you owe to others.
- Any lease or auto loan statements.
- Credit card statements.
- Amounts owed on mortgages or home equity lines of credit.
- Statements of any taxes owed.
- Installment loan statements, such as student loans or personal loans.
- Life insurance information.
- Any additional personal liabilities not listed above.
You can begin completing Form 413 once you’ve compiled the documentation. Let’s go over how to complete it step-by-step.
Select the SBA Loan
First, you’ll check off the SBA loan you’re applying for.
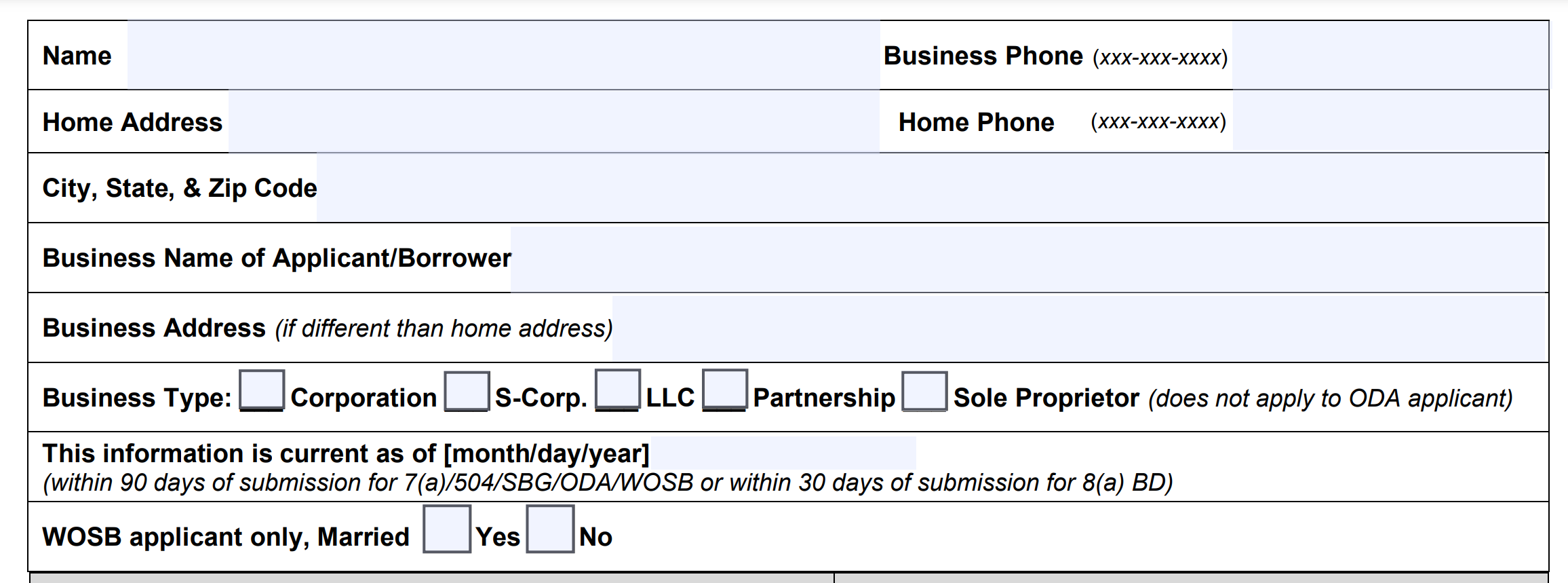
Enter Your Personal & Business Information
In this section, you’ll enter your name, contact information, the business’s name, contact information, and the type of business entity.
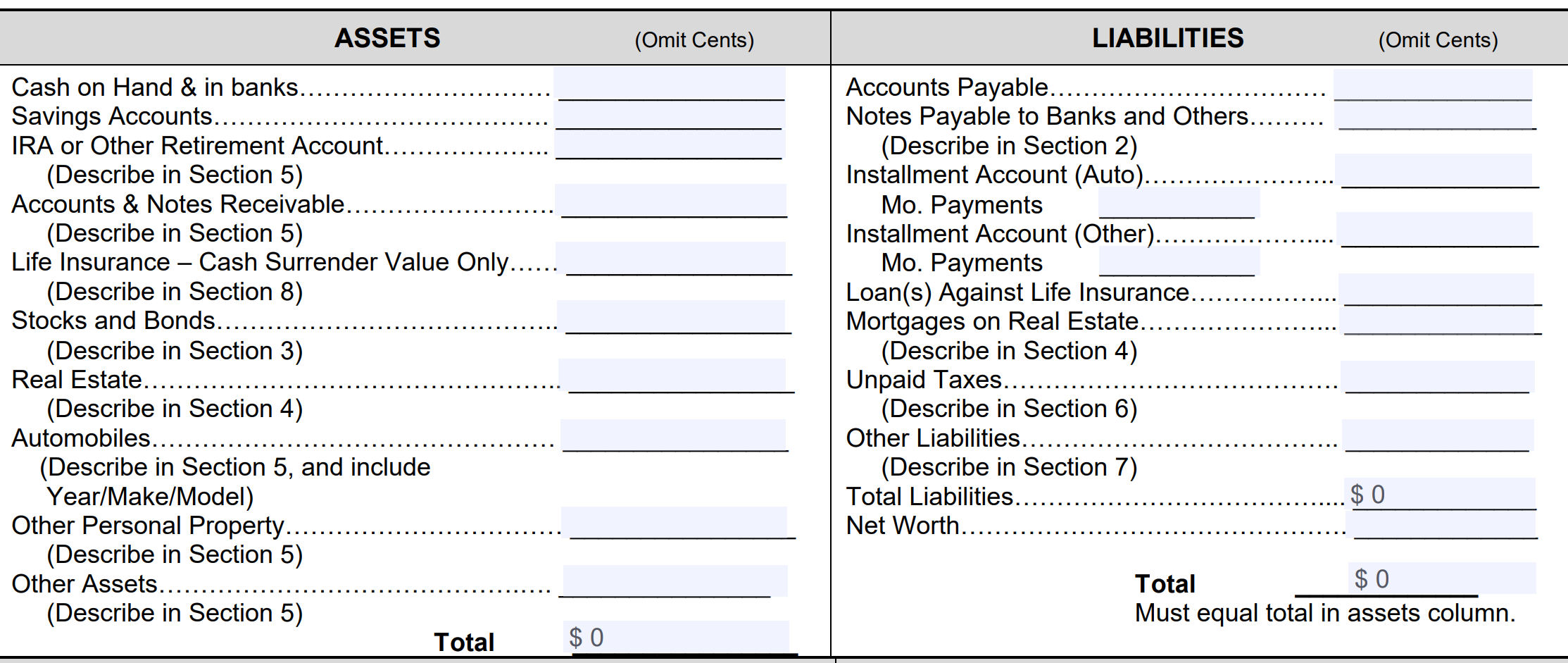
Asset & Liabilities
Next, list all your assets and liabilities.
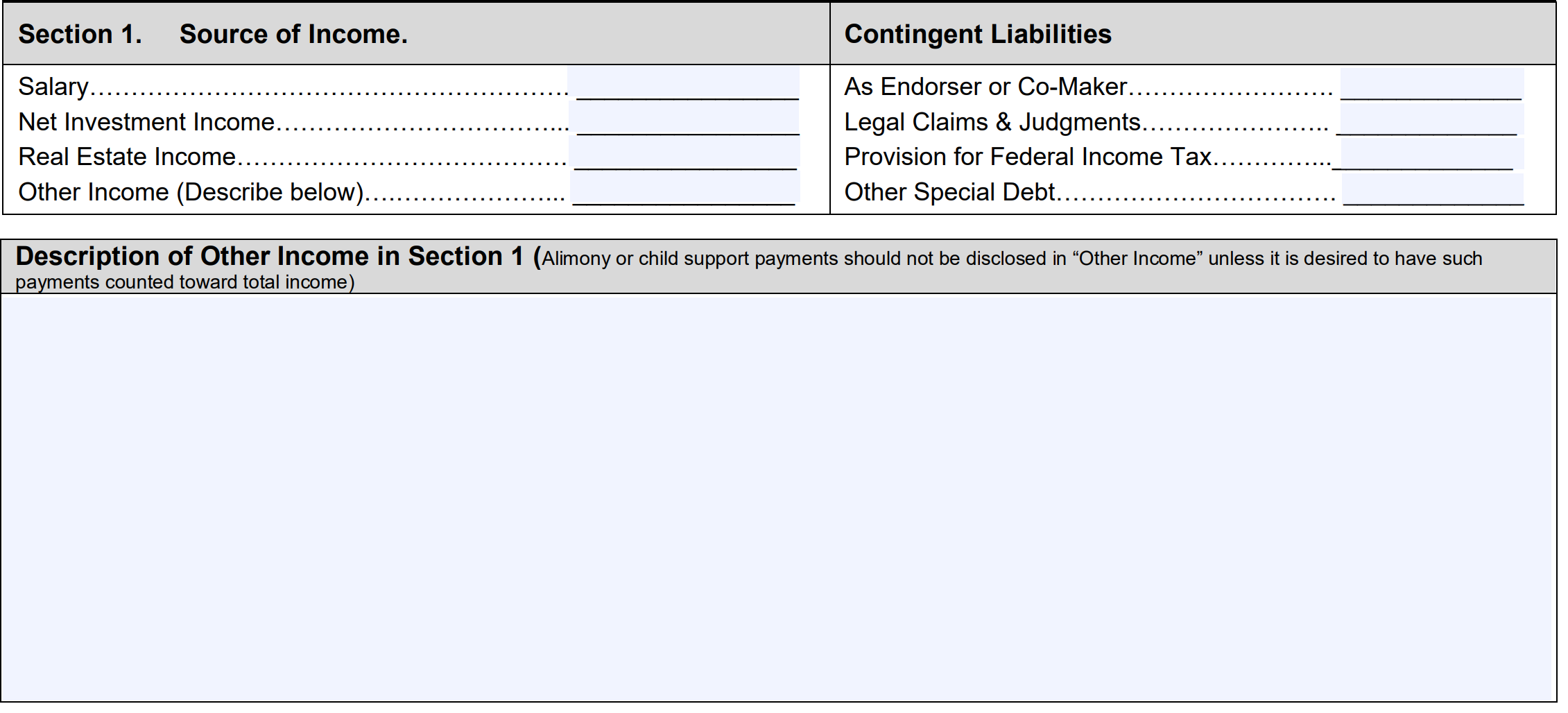
Section 1: Sources of Income
You’ll list any sources of income here. If you have a source of income not listed, write it in the “other income” section.
This section also requires you to list any contingent liabilities, which are debts you may incur pending the outcome of an event in the future. Examples include pending lawsuits or judgments. Another example would be if you co-signed on a loan, you could incur debt if the borrower defaults.
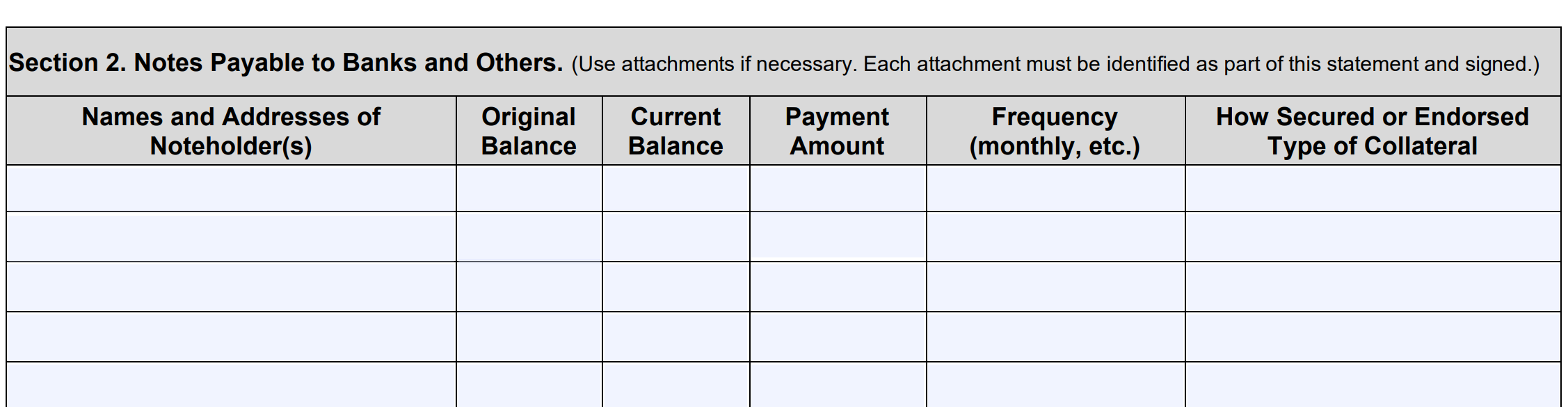
Section 2: Notes Payable to Banks and Others
Here you’ll list any debt owed from loans to banks or other lenders. You must indicate the original balance, current balance, and payment schedule. You’ll also identify if the loan is secured and, if so, what collateral you used to secure it.
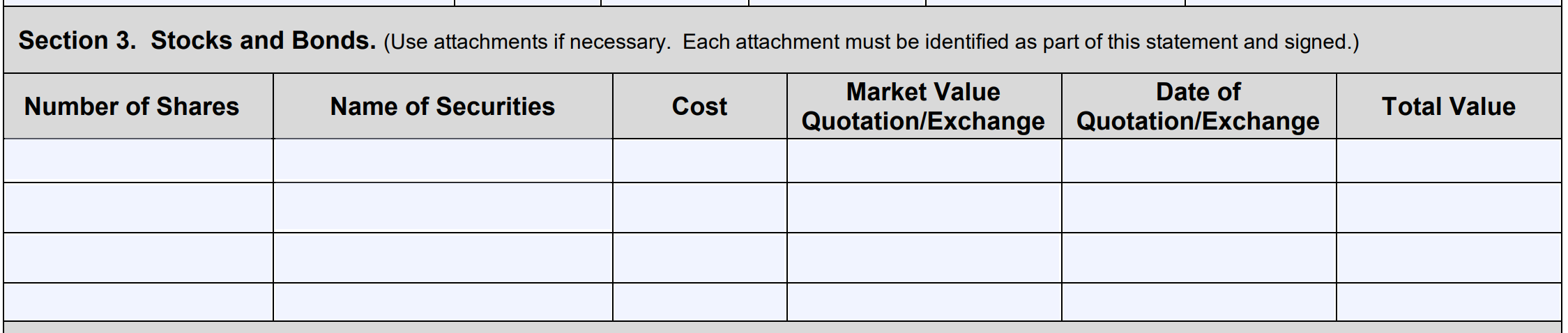
Section 3: Stocks and Bonds
Fill out any stocks or bonds you own in this section. Include the shares you own, your current market value, and the date of the current valuation. Per the form instructions, use attachments to include any stocks and bonds that could not fit in the space provided.
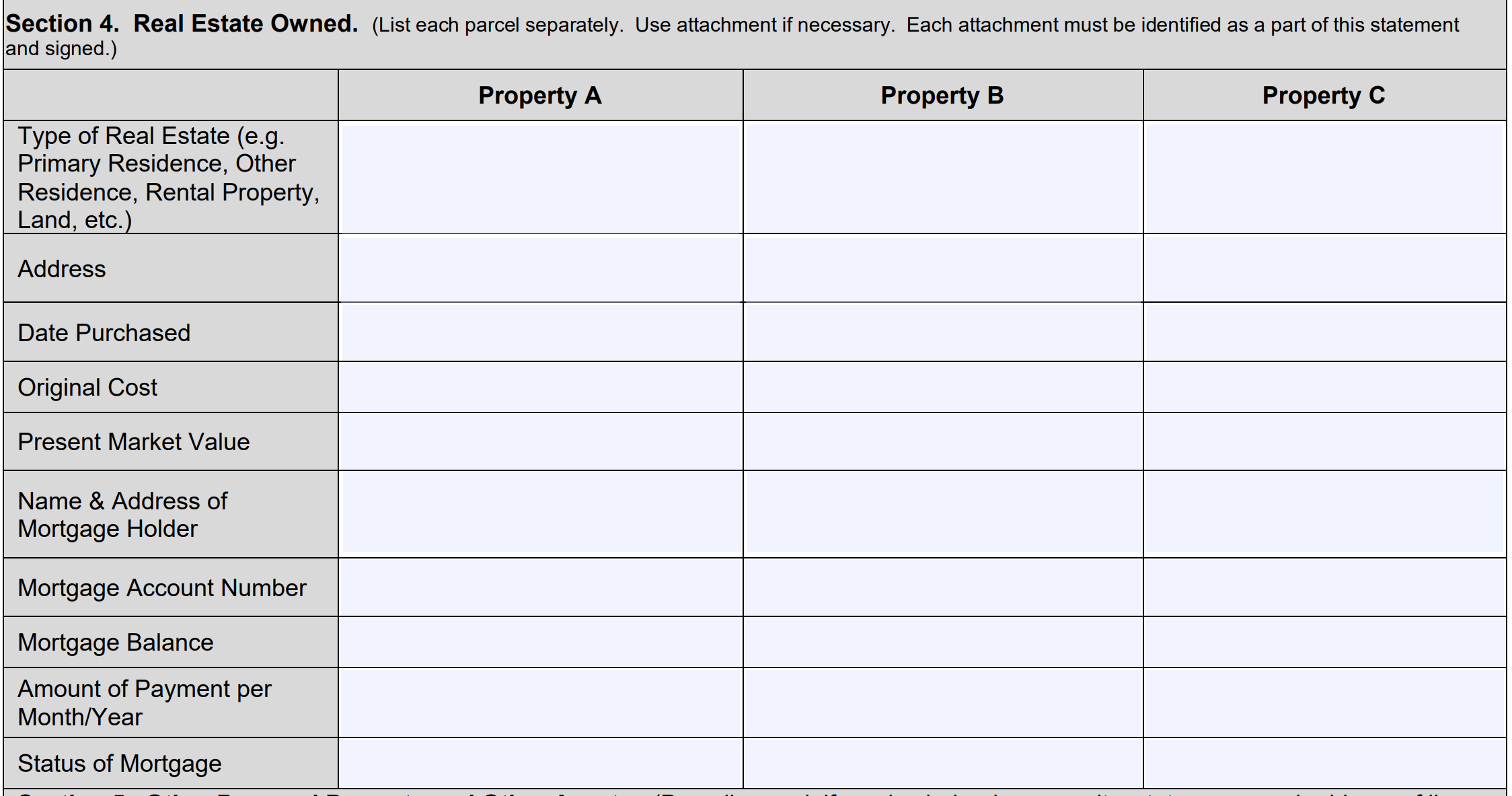
Section 4: Real Estate Owned
This section provides space to list up to three properties you own. You can use attachments if you have more than three to include. Follow the form instructions to identify key information for the three properties. Duplicate the same columns and rows in any attachments, if necessary.
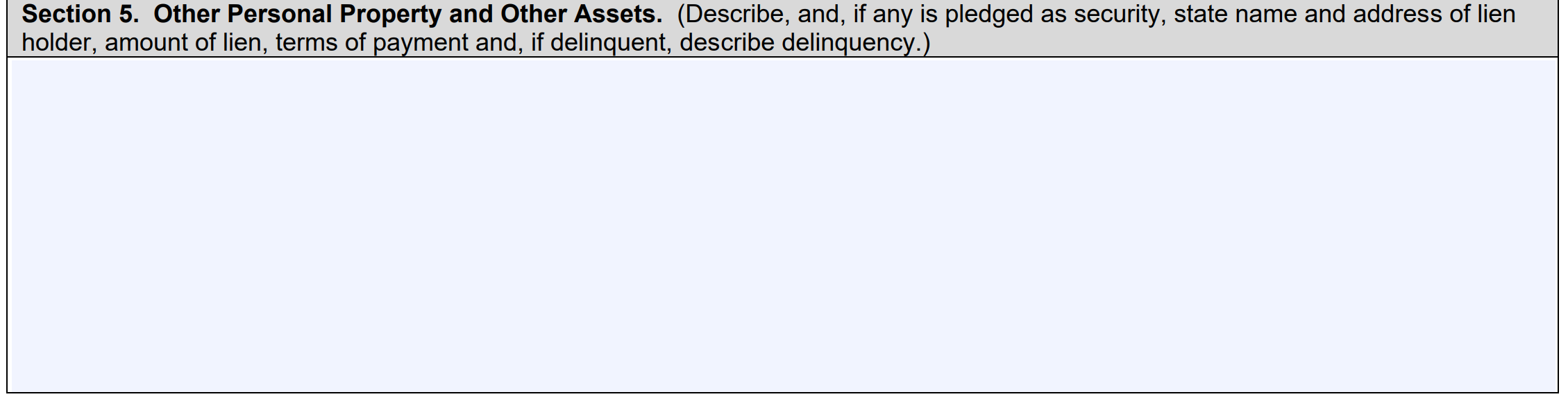
Section 5: Other Personal Property or Assets
Use this section to identify any other personal assets of value. Examples could include jewelry, artwork, or vehicles. List the make, model, and year, of any vehicle.
Section 6: Unpaid Taxes
In this section, you’ll expand on any unpaid taxes listed in the liabilities section at the beginning of the form. Include the type of tax, the amount owed, when they’re due, and any tax liens on the property. The SBA might request tax transcripts from the IRS to verify any tax information.
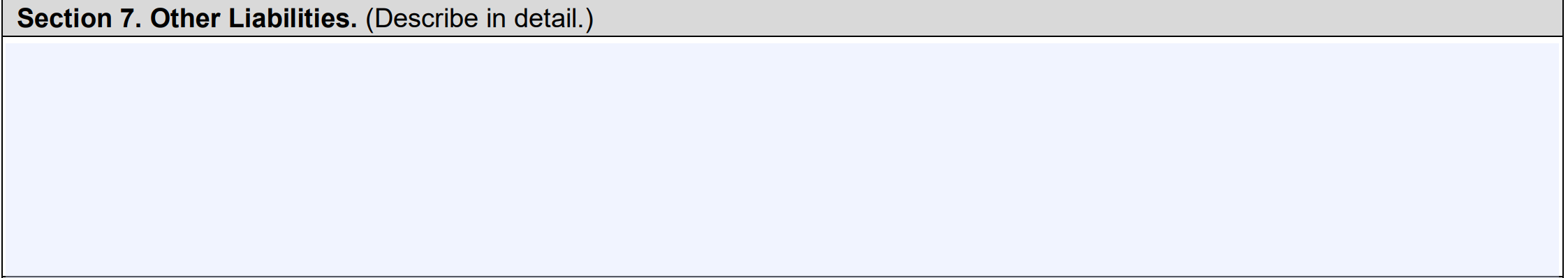
Section 7: Other Liabilities
Here you’ll list any additional liabilities not included in the sections above. Remember to only include liabilities for your personal finances.
Section 8: Life Insurance
In the final section, you’ll include any life insurance policy information. Include the insurer, type of life insurance, face amount, and the applicable cash surrender value upon cancellation of all your policies. List any beneficiaries as well.
Once you complete all the sections above, you’ll certify the form with your signature, social security number, and the date of the application. For SBA 7(a) loans, you’ll include the form with your application to the SBA lender. For SBA 504 loans, you’ll send the form to the Certified Development Company (CDC).
How to apply for an SBA Loan:
United Capital Source can help you apply to an SBA-approved lender following these steps.
Step 1: Ensure You Qualify
You’ll need a credit score between 650-700 and a healthy, consistent cash flow. How you intend to use the money plays a significant role as well.
Step 2: Gather Your Documents
Be prepared to provide:
- Driver’s License.
- Business license or certificate.
- Voided Business Check.
- Bank Statements.
- Credit Reports.
- Business Tax Returns.
- Credit Card Processing Statements.
- 3 Years of personal and business tax returns
- Personal Financial Statement.
- List of Real Estate Owned.
- Debt Schedule/Loan/Rent/Lease Documentation
- Deeds/Title/Ownership documentation for any collateral/Security
- Current Profit & Loss Statements and Balance Sheet Year-to-Date
- A/R and A/P Reports
- Business Plan.
- SBA Form 413.
- United Capital Source 1 Page Application
Step 3: Fill Out the Application
You can begin the application process by calling us or filling out our one-page online application. Either way, you’ll be asked to enter the information from the previous section along with your desired funding amount.
Step 4: Speak to a Representative
Once you apply, a representative will reach out to you to explain the repayment structure, rates, and terms of your available options. This way, you won’t have to worry about any surprises or hidden fees during repayment.
Step 5: Receive Approval
SBA Loans through our network generally take 3-5 weeks to process. Once approved and your file is closed, funds should appear in your bank account in a few business days.
What are the advantages of SBA Loans?
SBA loans are often considered the gold standard of small business financing. There are numerous advantages, but the biggest ones are the large borrowing amounts, low interest rates, and long repayment terms.
On-time SBA loan payments are reported to the major credit bureaus. Successfully paying your loan will help build your business credit, making it easier to secure financing in the future.
The low interest rate and long repayment terms mean your monthly payments are lower than most loan structures. This helps ensure you maintain strong cash flow during the life of the loan.
The high borrowing amounts allow businesses to make significant investments in their future. You can use the funds to acquire commercial real estate, hire more staff, purchase equipment and supplies, and more.
What are the disadvantages of SBA Loans?
The most significant disadvantage is the difficulty in getting approved. While you might assume that partially guaranteed loans are easier to qualify for, and it’s a logical assumption, the truth is often the opposite.
Since the SBA doesn’t provide concrete qualifications, lenders can set their own standards, and some are more stringent than others. For example, commercial banks are more biased toward established companies.
The loan application process also requires a lot of patience and having enough runway to wait for approval. Aspiring applicants might wait weeks to get a determination if the SBA will guarantee the loan.
It’s not uncommon to meet with several different lenders and submit multiple applications. Some lenders will tell applicants to try again in a year when finances have improved.
Pros & Cons
Pros:
- High borrowing amounts – up to $5 million.
- Low interest rates and long repayment terms.
- Can use the funds for a variety of business purposes.
Cons:
- Long application and approval process.
- Large amounts of paperwork.
- Might require collateral.
- Almost always requires a personal guarantee & down payment.
- Requires good-excellent credit.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are the most common questions about SBA Form 413.
What documentation do I need to prepare in addition to Form 413?
The exact documentation requirements depend on the lender and the specific SBA loan. In general, you should prepare any documents on personal or business assets and liabilities, personal and business tax returns, and any licenses, certificates, or other documents about your business. Contact the lender for any additional required documents.
What should I do if my liabilities are greater than my assets?
The SBA is most interested in your monthly debt liability and debt-to-income ratio (DTI), not your total net worth. If you have concerns about your financial situation, consider working with a loan expert to help guide you through the process.
What are my options if I don’t qualify for an SBA Loan?
While SBA Loans are the most advantageous small business loans, they are far from your only options. Many alternative lending platforms provide various loans with much looser requirements and significantly faster funding times.
You could consider any of the financing options:
- Working capital loans.
- Equipment financing.
- Merchant cash advance.
- Accounts receivable factoring.
- Revenue-based loans.
- Business lines of credit.
- Business term loans.
If you’ve been denied for credit reasons, bad credit business loan options are also available.
SBA Form 413 – Final Thoughts
SBA loans are the best small business financing options available, but the application process is tedious and time-consuming. Compiling the necessary documentation for completing 413 may be challenging, but it’s potentially worth it if it gets you the lowest-cost financing for your business.
Contact us if you need additional help with SBA Form 413 or if you’re ready to apply for an SBA loan. Our loan executives can help you start the process and answer any questions you have.